theraml框架框图
- thermal_zone_device:获取温度设备的抽象
- thermal_cooling_device: 降低温度措施的抽象
- thermal_governor:温控策略,step wise, bangbang,user space,power_allocator,fair_share
- thermal_core : 作为user space和kernel的接口,同时也是Thermal框架的中枢
相关的节点:/sys/class/thermal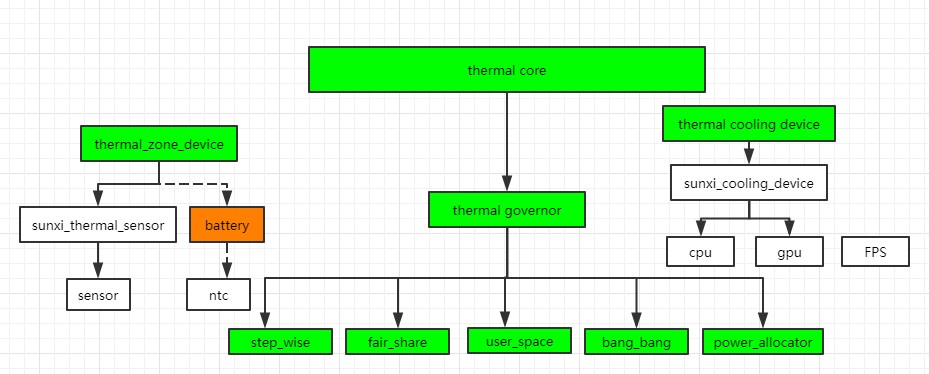
thermal_zone_device
dts
cpu_thermal_zone{
polling-delay-passive = <1000>;
polling-delay = <2000>;
thermal-sensors = <&ths_combine0 0>;
trips{
cpu_trip0:t0{
temperature = <65>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
cpu_trip1:t1{
temperature = <75>;
type = "passive";
hysteresis = <0>;
};
....
struct thermal_zone_of_device_ops {
int (*get_temp)(void *, int *);
int (*get_trend)(void *, int, enum thermal_trend *);
int (*set_trips)(void *, int, int); // 设置温度窗口,当温度超过设置点需要通过thermal_zone_device_update
int (*set_emul_temp)(void *, int);
int (*set_trip_temp)(void *, int, int);
};
struct thermal_zone_of_device_ops combine_ops = {
.get_temp = sunxi_combine_get_temp,
.set_emul_temp = sunxi_combine_set_emul_temp,
};
在probe中完成注册:
sensor->tz = thermal_zone_of_sensor_register(&pdev->dev,
id, sensor, &combine_ops);
温度获取流程
sunxi_combine_get_temp //sunxi_ths_combine.c
-->ret = controller->ops->get_temp(controller,sensor_id, &temp);
sunxi_ths_get_temp // sunxi_ths_core.c
-->t = ths_driver_get_temp(ths_data, id);
ths_driver_reg_to_temp(reg_data, id, ths_data->ths_driver_version, ths_data->ths_coefficent->calcular_para); //sunxi_ths_driver.c
thermal_core
在thermar core作为中枢注册governor,注册Thermal类,并且基于Device Tree注册Thermal Zone;提供Thermal zone注册函数,Cooling Device注册函数,提供将Cooling设备绑定到Zone的函数,一个Thermal Zone可以有多个Cooling设备;同时还提供一个核心函数Thermal_\zone_device\update作为Thermal中断处理函数和轮询函数,轮询时间会根据不同Trip Delay调节
1.thermal_init
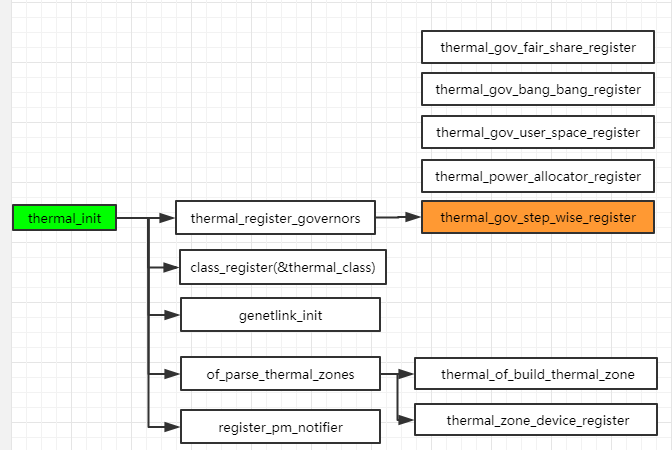
2.netlink
netlink是linux提供的用于内核和用户态进程之间通信的方式。一般来说用户空间和内核空间的通信方式有三种:/proc,ioctl,netlink,而前两种是单向的,但是netlink可以实现双工通信;虽然netlink主要用于用户空间和内核空间的通信,但是也能用于用户空间的两个进程通信。只是进程间通信有其他很多方式,除非需要用到netlink的广播特性;
netlink有以下特点:
1.支持全双工,异步通信(当然也同步也支持)
2.用户空间可使用标准的BSD socket接口
3.在内核空间使用专门的内核API接口
4.支持多播(因此支持”总线”式通信,可实现消息订阅)
5.在内核端可用于进程上下文和中断上下文;
用户态使用netlink:
用户态应使用标准的socket APIs,socket(),bind(),sendmsg(),recvmsg()和close()就可以使用netlink socket
netlink内核API
一:定义协议类型 (可省略)
二:netlink_kernel_create
三:设置目标地址与源地址
四:通过netlink_unicast和netlink_broadcast发送消息;
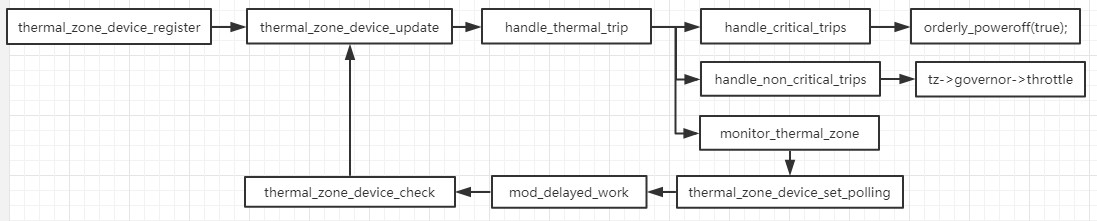
3.thermal轮询流程
在thermal core中通过不断的轮询来检测温度变化,如果温度没有达到crital则调用governor的throttle,通过governor的throttle决定下一次轮询的时间;如果温度为crital则走关机流程;
cooling_device
嵌入式设备通过改变频率电压,来达到改变功耗的目的,cooling_device提供了获取当前设备的温控状态以及设置等接口;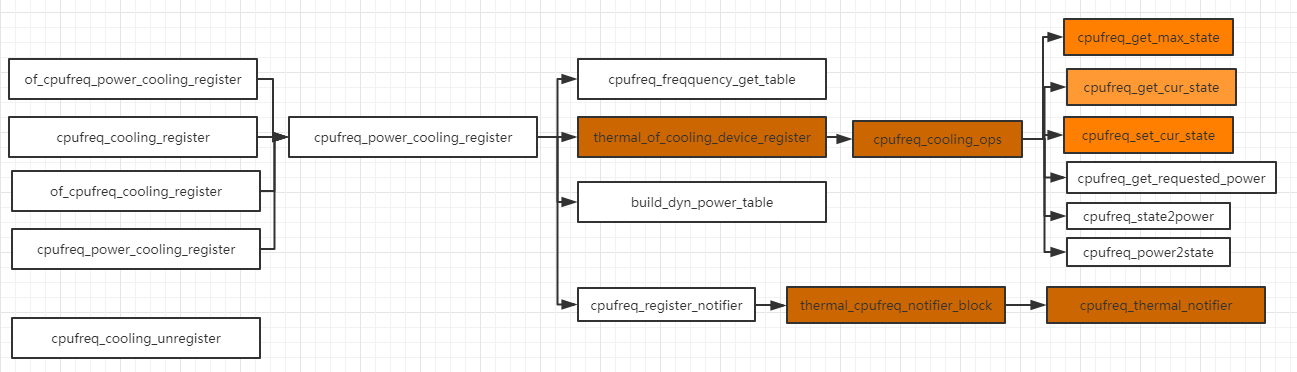
thermal_cooling_device
dts:
cooling-maps{
bind0{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip0>;
cooling-device
= <&cpu_budget_cooling 1 1>;
};
bind1{
contribution = <0>;
trip = <&cpu_trip1>;
cooling-device
= <&cpu_budget_cooling 2 2>;
};
...
cpu_budget_cooling:cpu_budget_cool{
compatible = "allwinner,budget_cooling";
device_type = "cpu_budget_cooling";
#cooling-cells = <2>;
status = "okay";
state_cnt = <7>;
cluster_num = <1>;
state0 = <1800000 4>;
state1 = <1512000 4>;
state2 = <1416000 4>;
state3 = <1200000 4>;
state4 = <1008000 3>;
state5 = <1008000 2>;
state6 = <1008000 1>;
};
...
struct thermal_cooling_device_ops {
int (*get_max_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *); //获取最高的cooling状态的回调函数,指最低功耗的OPP
int (*get_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long *); //获取当前cooling状态的回调函数
int (*set_cur_state) (struct thermal_cooling_device *, unsigned long); //根据cooling_state执行cpufreq的回调函数,是执行的实体
int (*get_requested_power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32 *);//获取当前当前CPU的功耗值,包括dynamic功耗和static功耗。中间需要用到dyn_power_table进行转换
int (*state2power)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, unsigned long, u32 *); //将CPU cooling状态转换成需要消耗的功耗值;
int (*power2state)(struct thermal_cooling_device *,
struct thermal_zone_device *, u32, unsigned long *);//将CPU所能获取的最大功耗值转换成cooling状态
};
static struct thermal_cooling_device_ops const sunxi_cpu_cooling_ops = {
.get_max_state = cpu_budget_get_max_state,
.get_cur_state = cpu_budget_get_cur_state,
.set_cur_state = cpu_budget_set_cur_state,
};
cool_dev = thermal_of_cooling_device_register(
pdev->dev.of_node,
SUNXI_BUDGET_COOLING_NAME,
budget_cdev,
&sunxi_cpu_cooling_ops);
set_cur_state
->cpu_budget_apply_cooling(cooling_device, state);
->sunxi_hotplug_update_state(cooling_device, cluster);
->autohotplug_roomage_limit(cluster, min, max); //限制最大的核数
->sunxi_cpufreq_update_state(cooling_device, cluster); ??怎么传递这个参数的
->cpufreq_update_policy(cpuid); //限制最大频率
thermal governor
内核中的governor策略
step wise: Open loop control. Temperature threshold and trend based. Walk through each cooling device cooling state, step by step.
fair share: Weight based. Determine the cooling device state based on assigned weight partitioning.
bang bang: uses a hysteresis to switch abruptly on or off a cooling device. It is intended to control fans, which can not be throttled but just switched on or off.
power allocator: Closed loop control. Based on power budget, temperature, and current power consumption of each involved device.
user space: hand off the control of a thermal zone to user space. Example: thermald and iTux.
手机端的thermal配置情况
mtk
以魅族 15plus为例
15Plus:/sys/class/thermal $ ls
cooling_device0 cooling_device2 cooling_device4 cooling_device6 thermal_zone1 thermal_zone3 thermal_zone5\
cooling_device1 cooling_device3 cooling_device5 thermal_zone0 thermal_zone2 thermal_zone4
cooling device
15Plus:/sys/class/thermal/cooling_device1 $ ls
cur_state max_state power subsystem type uevent
for i in $(seq 0 6)
do
printf "cooling_device$i\t"
type=$(cat cooling_device$i/type)
printf "$type\t"
cur_state=$(cat cooling_device$i/cur_state)
printf "$cur_state\t"
max_state=$(cat cooling_device$i/max_state)
printf "$max_state\n"
done
cooling_device0 battery_control02 0 1
cooling_device1 battery_control01 0 1
cooling_device2 battery_control00 0 1
cooling_device3 thermal-cpufreq-0 0 13
cooling_device4 thermal-cpufreq-1 0 8
cooling_device5 thermal-gpufreq-0 0 4
cooling_device6 thermal-isp-0 0 2
thermal_zone
for i in $(seq 0 5)
do
printf "thermal_zone$i\t"
type=$(cat thermal_zone$i/type)
printf "$type\t"
policy=$(cat thermal_zone$i/policy)
printf "$policy\n"
done
thermal_zone0 mngs-thermal power_allocator cdev【0-1】 -> ../cooling_device3 thermal-cpufreq-0
thermal_zone1 APOLLO step_wise cdev【0-4】 -> ../cooling_device4 thermal-cpufreq-1
thermal_zone2 GPU power_allocator cdev【0-1】 -> ../cooling_device5 thermal-gpufreq-0
thermal_zone3 ISP step_wise cdev【0-4】 -> ../cooling_device6 thermal-isp-0
thermal_zone4 battery step_wise
thermal_zone5 meizu_ntc step_wise cdev【0-2】 -> ../cooling_device【0-2】 battery_control0【0-2】
海思
以荣耀9为例
cooling_device
cooling_device0 thermal-devfreq-0 05
cooling_device1 thermal-cpufreq-0 04
cooling_device2 thermal-cpufreq-1 04
thermal_zone
thermal_zone0 soc_thermal power_allocator cdev【0-2】 -> ../cooling_device[0-2]
thermal_zone1 Battery user_space
thermal_zone2 cluster0 user_space
thermal_zone3 cluster1 user_space
thermal_zone4 gpu user_space
thermal_zone5 modem user_space
thermal_zone6 ddr user_space
thermal_zone7 system_h user_space
thermal_zone8 flash_led user_space
thermal_zone9 charger user_space
thermal_zone10 pa_0 user_space
thermal_zone11 dcxo0 user_space
thermal_zone12 hisi_shell user_space
thermal_zone13 hisi_ambient user_space
高通
以pixel为例
cooling_device
type cur_state max_state
cooling_device0 thermal-cpufreq-0 1900800 21
cooling_device1 thermal-cpufreq-1 2457600 30
thermal_zone
thermal_zone0 mnh_ipu1 step_wise
thermal_zone1 mnh_ipu2 step_wise
thermal_zone2 mnh_cpu step_wise
thermal_zone3 mnh_lpddr step_wise
thermal_zone4 usb step_wise
thermal_zone5 battery step_wise
thermal_zone6 usb_port_temp step_wise
thermal_zone7 pm8998_tz step_wise
thermal_zone8 pmi8998_tz step_wise
thermal_zone9 pm8005_tz step_wise
thermal_zone10 msm_therm step_wise
thermal_zone11 quiet_therm step_wise
thermal_zone12 xo_therm step_wise
thermal_zone13 fpc_therm step_wise
thermal_zone14 back_therm step_wise
thermal_zone15 pa_therm step_wise
thermal_zone16 tsens_tz_sensor0 step_wise
thermal_zone17 tsens_tz_sensor1 step_wise
thermal_zone18 tsens_tz_sensor2 step_wise
thermal_zone19 tsens_tz_sensor3 step_wise
thermal_zone20 tsens_tz_sensor4 step_wise
thermal_zone21 tsens_tz_sensor7 step_wise
thermal_zone22 tsens_tz_sensor8 step_wise
thermal_zone23 tsens_tz_sensor9 step_wise
thermal_zone24 tsens_tz_sensor10 step_wise
thermal_zone25 tsens_tz_sensor11 step_wise
thermal_zone26 tsens_tz_sensor12 step_wise
thermal_zone27 tsens_tz_sensor13 step_wise
thermal_zone28 tsens_tz_sensor14 step_wise
thermal_zone29 tsens_tz_sensor15 step_wise
thermal_zone30 tsens_tz_sensor16 step_wise
thermal_zone31 tsens_tz_sensor17 step_wise
thermal_zone32 tsens_tz_sensor18 step_wise
thermal_zone33 tsens_tz_sensor19 step_wise
thermal_zone34 tsens_tz_sensor20 step_wise
thermal_zone35 tsens_tz_sensor21 step_wise
thermal_zone36 limits_sensor-00 step_wise
thermal_zone37 limits_sensor-01 step_wise
thermal_zone38 bcm15602_tz step_wise
thermal_zone39 bms step_wise
thermal_zone40 GLM_soc step_wise
通过观察发现,power allocator,step wise,user space为常用的governor,故以下简单介绍此三种thermal;
Power allocator
IPA的发展历史
在2013,ARM 开始在Linux OS中布局IPA,只是介绍了相关的概念和在实际场景中的好处;
在2015年3月3号,第一个完整的IPA提交被纳入Linux,并被merge到linux4.2.所以linux4.2之后不用再打相关的pactch
在讲power allocator 前,需要先讲个概念PID(Proportional Integral Derivative)的概念;
PID控制器
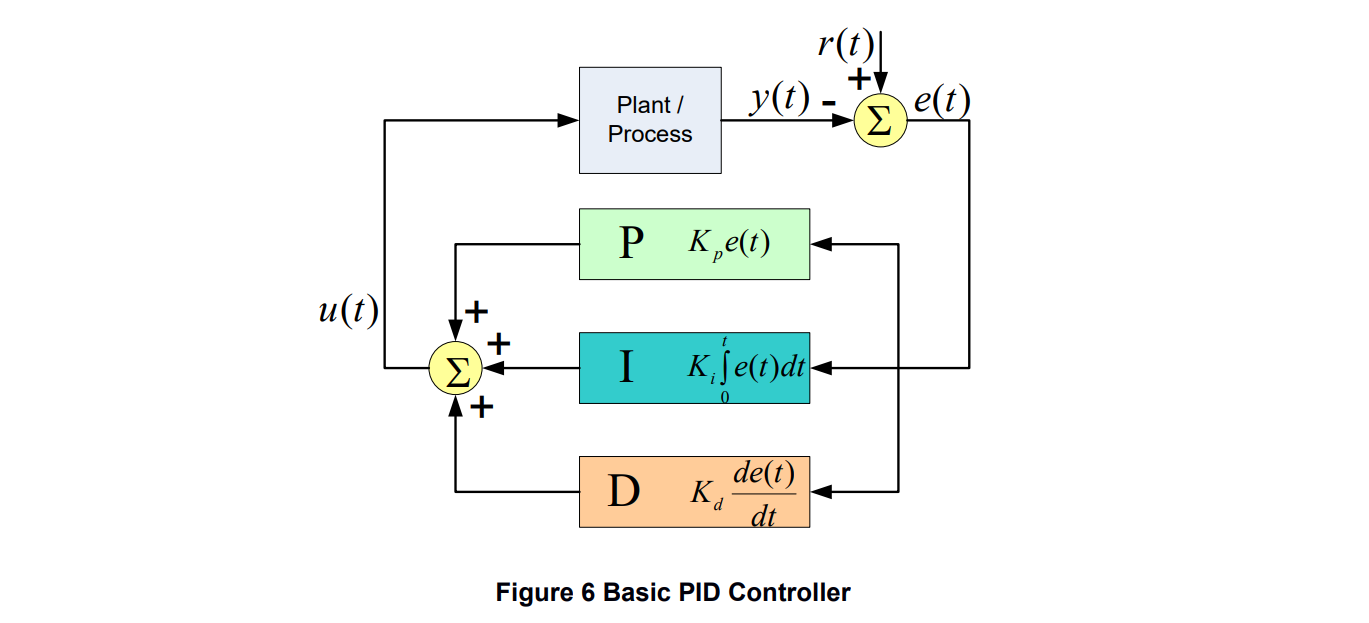
PID控制器是一个闭环的系统,通过将输出反馈到输入,这使系统可以得到更精细和自适应的控制
.u(t) is the control signal.
.y(t)is the actual output value.
.r(t) is the reference value, also called the setpoint. It is the desired output value.
.e(t) is the control error (e(t) = r(t) − y(t)). It shows the difference between the reference value and the actual output value.
.The term Plant refers to the object that is being controlled
The control signal 𝑢(𝑡) is a sum of the following terms:
The P-term: This term is proportional to the error. It acts on the present value of the error.
The I-term: This term is proportional to the integral of the error. It represents the accumulation of past errors.
The D-term: This term is proportional to the derivative of the error. It can be interpreted as a prediction of future errors, based on linear extrapolation according to the current rate of change.
PID控制器适用于多个控制领域,除了多路输入输出;
对于thermal 而言,对应的PID如以下模样:
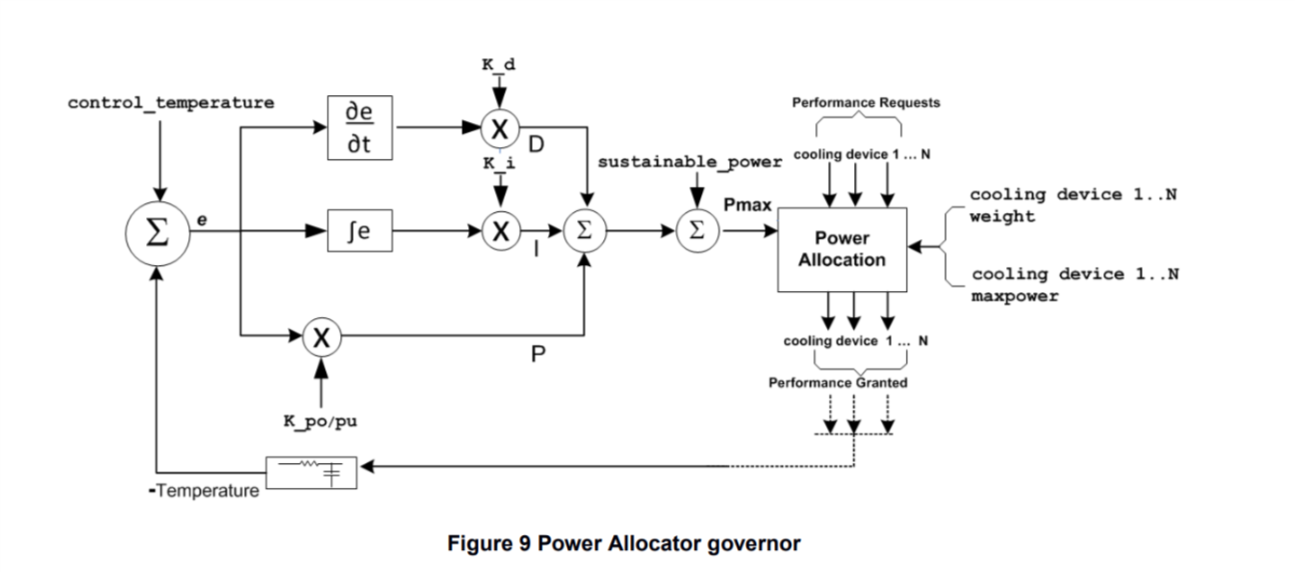
Pmax 是根据当前的温度和预想的温度计算出来的系统可以运行的最大功耗:
计算公式如下:
P_max = k_p * e + k_i * err_integral + k_d * diff_err + sustainable_power
e = desired_temperature - current_temperature
err_integral is the sum of previous errors
diff_err = e - previous_error
. 所谓的Sustainable Power是在不同OPP情境下,某一个最大的OPP的温度保持基本稳定,比其大者,温度上升明显;比其小者温度保持不变或者下降;这可以通过监测不同OPP对应的温度值,得到一个Sustainable Power
以荣耀9为例:
Sustainable Power = 4500
trip_point_1_temp = 80000;
trip_point0_temp = 55000;
if (!tz->tzp->k_po || force)
tz->tzp->k_po = int_to_frac(sustainable_power) / temperature_threshold;
k_po = sustainable_power / (desired_temperature - switch_on_temp) = (4500 * 1024)/(80000-55000) = 184.32
if (!tz->tzp->k_pu || force)
tz->tzp->k_pu = int_to_frac(2 * sustainable_power) / temperature_threshold
k_pu = 2 * sustainable_power / (desired_temperature - switch_on_temp) = = (2 * 4500 * 1024)/(80000 - 55000) = 368.64;
tz->tzp->k_i = int_to_frac(10) / 1000 = 10.24;
k_i = 10 * 1024 /1000 = 为积分常数,用来补偿偏移;当温度误差低于 integral_cutoff(一般为0)误差就会被累计
k_d 为求导,一般设置为0
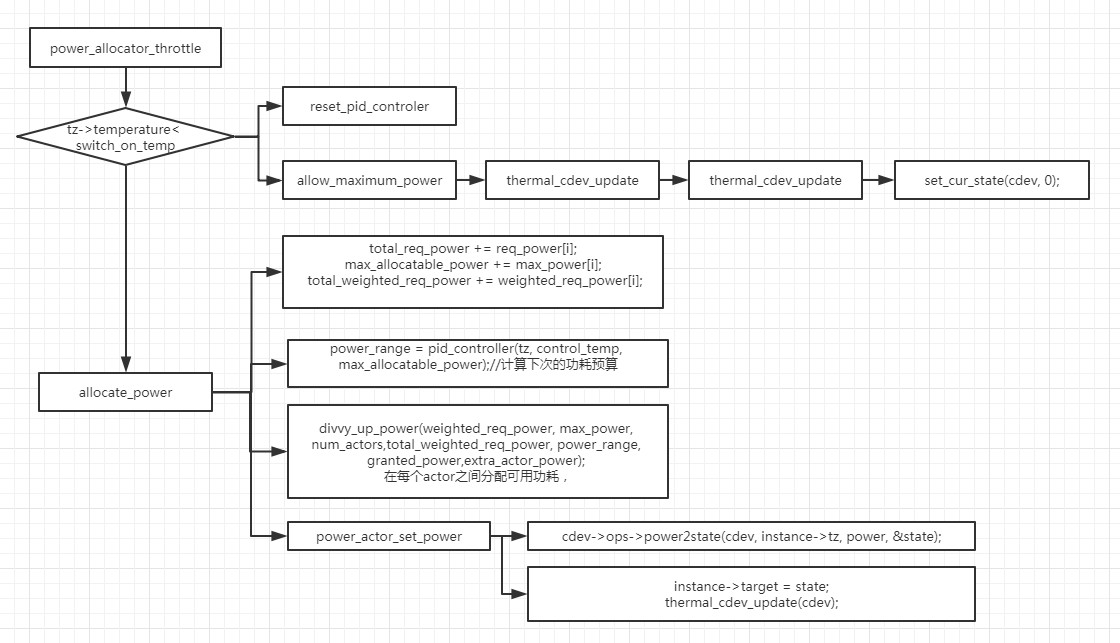
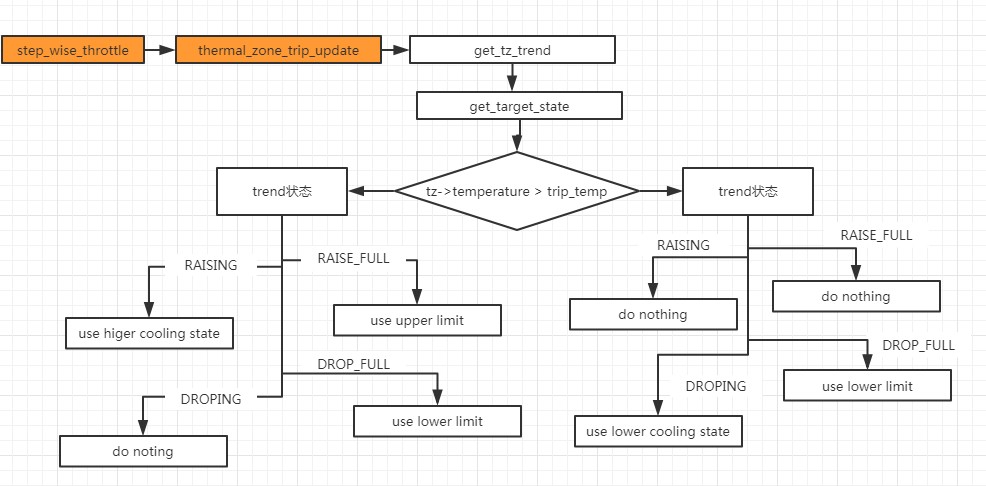
step wise
根据当前温度的趋势(上升,下降)和与当前的trip温度对比,来决定CPU下一次的cooling状态
user space
通过将温度,事件,暴露到上层,上层应用再去驱动throttle进行控温,目前没有相关的资料可以分析,暂时不做分析;
参考资料
Android/Linux Thermal框架分析及其Governor对比
Android/Linux Thermal Governor之IPA分析与使用
内核启动参数,模块参数与sysfs,sysctl,系统调用和netlink